Bank storage = new uses for teeth
When a baby tooth is about to fall out, when you need to have a tooth removed for orthodontic straightening, or when wisdom tooth removed is recommended… what do you do with that tooth?
If it’s a baby tooth, you might throw it on the roof or bury it in the soil in the hopes that the next tooth will grow in beautifully, or put it in a storage case and store it away carefully.
In the case of adult teeth, many people say they don’t know what happens to their teeth after they are removed by the dentist.
While some people may take them home as souvenirs, most of these teeth are simply discarded.

Tissue / cell bank storage is a new use for discarded teeth.
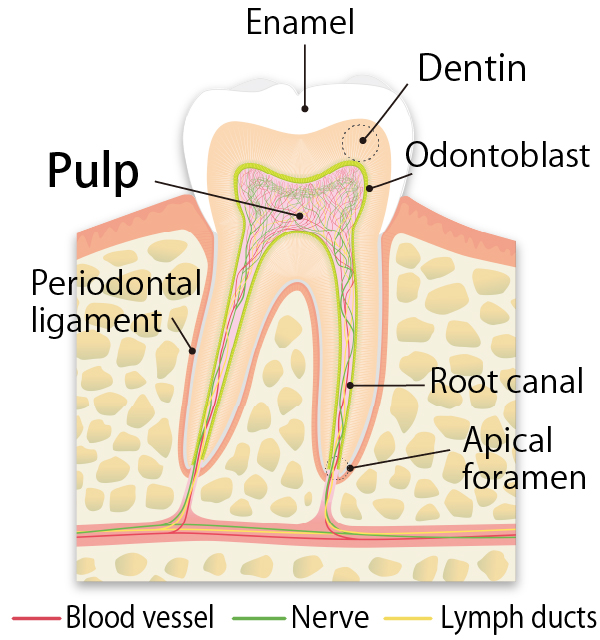
Teeth contain a tissue called dental pulp, which is a collection of blood vessels that carry nutrients to the teeth, and nerves that sense temperature and pain. This dental pulp contains pulp stem cells, which have the function of regenerating nerves, blood vessels, and other tissues. (Dental pulp stem cells have been attracting attention as a “trump card” in regenerative medicine in recent years.)
Our Dental Tissue Bank, Dental Pulp Stem Cell Bank, and Dentin Bank services can be used to freeze and store the youngest healthy cells and tissues in your life now, in preparation for future regenerative medicine, to protect yourself and your family in the future.
The fact that our dental pulp regenerative treatment has already been used in practice – is another advantage of our service.
Why do we need a tissue / cell bank?
– Two major advantages of storing teeth in a tissue / cell bank –
1. Tissue / cells may be used for regenerative medicine in the future
What are the benefits of storing dental pulp tissue, dental pulp stem cells, and dentin tissue in a tissue / cell bank?
The biggest advantage is the possibility of using them for regenerative medicine.
Regenerative medicine refers to medical treatments in which cells (or tissues produced from cells) are transplanted into body tissues that have been damaged by injury or illness, in an attempt to restore bodily functions to a normal (or near-normal) state.
One kind of cells used in regenerative medicine are the dental pulp stem cells contained in dental pulp tissue.
One kind of cells used in regenerative medicine are the dental pulp stem cells contained in dental pulp tissue.
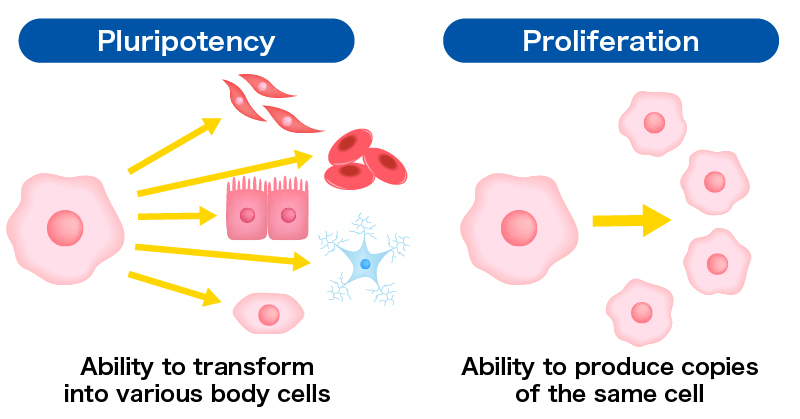
Dental pulp stem cells have the ability to transform into various body cells (pluripotency), and to divide and produce copies of the same cell with that pluripotency (self-replication and proliferation).
These abilities are attracting attention in the field of regenerative medicine, and various research is being conducted.
In Japan, efforts are underway to implement practical applications of regenerative medicine so that it can be used in medical treatment in a safe and reliable manner, such as with the enactment of the Act on the Safety of Regenerative Medicine, etc., in 2014.
In 2020, our research and development of dental pulp regenerative treatment, which regenerates “dental nerves” (dental pulp) lost due to severe tooth decay or trauma, was put into practical use as a familiar form of regenerative medicine.
Depositing dental pulp stem cells in a cell bank makes it possible to regenerate healthy teeth (dental pulp) when other teeth become decayed in the future.
Today, dentin regeneration in the crown of the tooth has also been successfully performed by transplanting fragments of dentin tissue collected from extracted teeth during pulp regenerative treatment.
In this way, dental pulp tissue, dental pulp stem cells, and dentin tissue deposited with our tissue /cell bank storage services can be used in treatment to regenerate healthy teeth (dental pulp) when other teeth become decayed.


2. Current young stem cells can be preserved
Although stem cells in teeth have the ability to replicate and proliferate, they do not continue to multiply indefinitely.
Since the ability to proliferate declines with age, storing tissues and stem cells in a bank now, while they are healthy, allows them to be used for future treatments.
We use liquid nitrogen to store dental pulp stem cells and pulp tissues, which are frozen in their healthy state and stored in storage containers kept at temperatures of -150°C and below.
When they are needed for regenerative treatments, tissues and cells are removed from their storage containers, thawed, and process to required amount and state.

Another advantage of using a tissue / cell bank is that you can store your current cells like a time capsule, because the healthy cells you store in your 20s can be used for treatment in your 50s and 60s.
Before depositing tissue / cells in a bank: four common questions
1. Can I only deposit adult teeth? How about baby teeth?
If extraction does not affect your bite, and the pulp is healthy, it is possible to bank both permanent (adult) and deciduous (baby) teeth.
- Baby teeth that are about to fall out.
- Teeth scheduled for extraction due to orthodontic straightening
- Wisdom teeth
and so on are all eligible for depositing.
(Depending on the condition of the tooth, such as when a wisdom tooth grows at an angle or if there is severe tooth decay, it may be difficult to deposit the tooth in a bank.)
【About baby teeth】
In the case of deciduous (baby) teeth, the front teeth are very small, and the size of pulp in the tooth is also very small, so it may not be possible to collect the amount of tissue required to create a cell culture.
We therefore recommend using the third to fifth teeth from the front.
Dental pulp stem cells contained in deciduous teeth are said to have a higher proliferative ability than permanent teeth, and are thought to be able to produce more cells.
Of course, pulp stem cells taken from permanent (adult) teeth can also have good proliferation, although there are individual differences in proliferative ability.

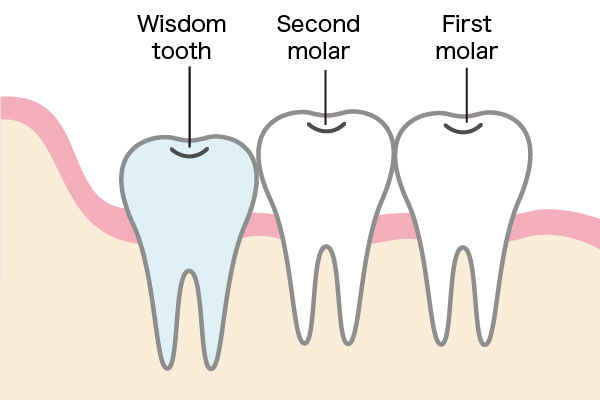
【About wisdom teeth】
Some asked if we should remove wisdom teeth.
Wisdom teeth are the most posterior teeth (furthest back) on the top, bottom, left and right sides, and are the eighth tooth counted from the front teeth.
Not everyone has wisdom teeth, and there are many different patterns; such as those who have all four, those whose wisdom teeth are buried in the gums, and those who do not have any wisdom teeth at all.
If you have healthy wisdom teeth, there is no need to extract them just for the sake of it. But depending on how your wisdom teeth grow, they may become difficult to brush, and may become prone to tooth decay.
If you are feeling pain or are otherwise concerned about your wisdom teeth, please consult with your dentist.
2. Is there an age limit for storing teeth in a bank?
There is no age limit. Anyone can use our tissue or cell banks, regardless of age or gender.
In general, as people grow older, the amount of pulp in their teeth decreases, and the rate of cell proliferation also tends to decrease.
We therefore recommend extracting and depositing teeth as early as possible (i.e., as young as possible) when considering the timing for depositing tissue and cells in a bank.
There is also no age-based storage period for dental pulp tissue, pulp stem cells, and dentin tissue stored in our banks.
The initial storage period is five or ten years, but if you wish to renew, you can continue to store tissue and cells in our banks for 20 or 30 years.

3. Are there any special procedures required? How do I go about depositing material in a tissue / cell bank?
Firstly, there is no need for hospitalization or any other special procedures.
You need only to have your tooth extracted at one of our partner dental clinics, after signing a contract with us. You don’t have to do anything else.
The extracted tooth will be sent from the partner dental clinic to our Cell Processing Center (CPC), where pulp tissue and pulp stem cells are isolated from the tooth and stored cryogenically (by freezing).
A list of partner dental clinics nationwide is available here.
Please check the list, and contact us if you do not see any partner dental clinics in your area

4. Can I deposit teeth that have fallen out naturally, or that have been stored in the refrigerator?
For tissue / cell banking, it is necessary to remove the dental pulp tissue and isolated the pulp stem cells in a clean environment while they are still alive after tooth extraction for the cell culture to be successful.
In the case of teeth that have fallen out naturally or have been stored in a refrigerator, there is a high possibility that various bacteria will adhere to the pulp, and it will not be able to be cultured.
In addition, since the proliferative ability of pulp stem cells in extracted teeth may be weakened with time, we ask that you send them to us immediately after extraction and cleaning at a partner dental clinic.

Extracted teeth are a gift to future family members
We are currently conducting research to enable stored tissues and stem cells to be used not only by the individuals who deposit them, but also by their family members.
We are currently engaged in research on pulp regenerative treatments that in a few years, we will be able to regenerate pulp using pulp stem cells from family members up to a second degree of kinship.
We are also seeking to expand into the cosmetic field, and the medical application for conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and cerebral infarction (stroke).
By depositing a tooth in the dental pulp stem cell bank, our aim is to enable your family members who have not deposited their own unneeded teeth (wisdom teeth and baby teeth, etc.) to receive various treatments in the future.
Regenerative medicine will continue to develop, and the uses of dental pulp stem cells will continue to increase in the future.
In the era of 100-year lifetime, it is important to live in your own way, while maintaining a healthy body.
Why not take this opportunity to consider storing a tooth in our tissue / cell bank now, as a gift to your future self and your future family?

